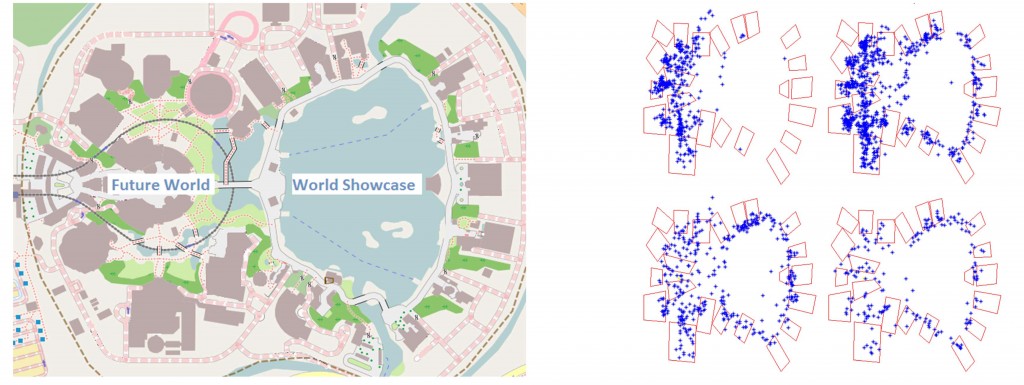
Performance of Collaborative GPS Localization in Pedestrian Ad Hoc Networks
In ad hoc networks without static nodes that could be used as reference points, mobile handhelds must rely on their GPS receivers to enable location-aware services.
March 15, 2012
ACM International Workshop on Mobile Opportunistic Networks (ACM MobiOpp) 2012
Authors
Vladimir Vukadinovic (Disney Research)
Stefan Mangold (Disney Research)
Performance of Collaborative GPS Localization in Pedestrian Ad Hoc Networks
In ad hoc networks without static nodes that could be used as reference points, mobile handhelds must rely on their GPS receivers to enable location-aware services. By sharing their position estimates using short range radios, neighboring devices may suppress unnecessary GPS activations in order to reduce energy consumption. We describe and evaluate two collaborative GPS localization protocols based on substitution and averaging of position estimates. The evaluation focuses on entertainment park scenarios and relies on realistic simulations to capture the mobility of park visitors. We demonstrate that the simple collaboration protocols, which do not require distance estimation between the neighbors, may provide significant energy savings. We discuss the impact of device density and provide guidelines for choosing the transmission range of their radio interfaces.