Theory, Analysis and Applications of 2D Global Illumination
We propose second-order Taylor expansion from cache points, which results in more accurate irradiance reconstruction.
August 6, 2012
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2012
Authors
Wojciech Jarosz (Disney Research/University of California, San Diego)
Volker Schönefeld (RWTH Aachen University)
Leif Kobbelt (RWTH Aachen University)
Henrik Wann Jensen (University of California, San Diego)
Theory, Analysis and Applications of 2D Global Illumination
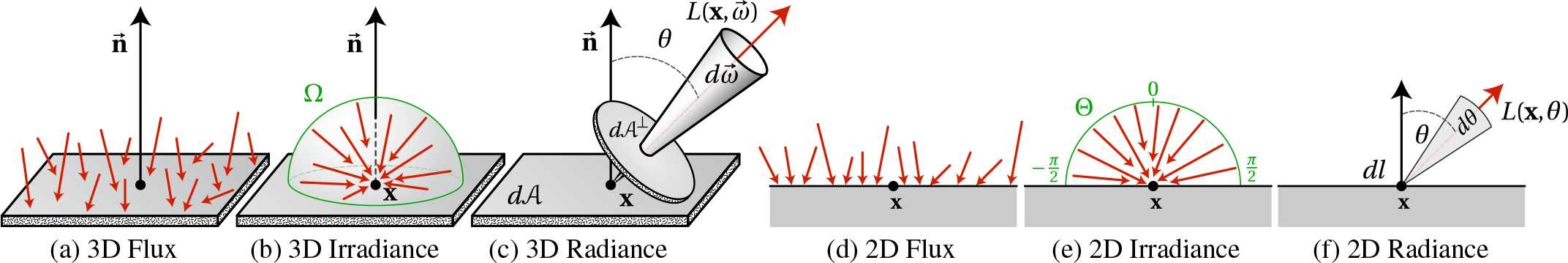
We investigate global illumination in 2D and show how this simplified problem domain leads to practical insights for 3D rendering. We first derive a full theory of 2D light transport by introducing 2D analogues to radiometric quantities such as flux and radiance and deriving a 2D rendering equation. We use our theory to show how to implement algorithms such as Monte Carlo ray tracing, path tracing, irradiance caching, and photon mapping in 2D, and demonstrate that these algorithms can be analyzed more easily in this domain while still providing insights for 3D rendering. We apply our theory to develop several practical improvements to the irradiance caching algorithm. We perform a full second-order analysis of diffuse indirect illumination, first in 2D, and then in 3D by deriving the irradiance Hessian, and show how this leads to increased accuracy and performance for irradiance caching. We propose second-order Taylor expansion from cache points, which results in more accurate irradiance reconstruction. We also introduce a novel error metric to guide cache point placement by analyzing the error produced by irradiance caching. Our error metric naturally supports anisotropic reconstruction and, in our preliminary study, resulted in an order of magnitude less error than the “split-sphere” heuristic when using the same number of cache points.