Circuit Model for Resonant Cavity Mode Enabled Wireless Power Transfer
In this work a general circuit model for the cavity resonant wireless power system is introduced and validated against simulated and measured results.
October 4, 2016
The European Microwave Conference 2016
Authors
Mohsen Shahmohammadi (Disney Research)
Matt Chabalko (Disney Research)
Alanson Sample (Disney Research)
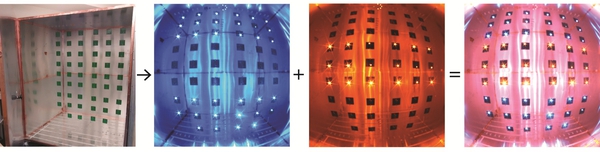
Recently, a new paradigm in wireless power transfer based on cavity mode resonance has experimentally shown the ability to efficiently deliver power to multiple receivers over large 3D volumes of an enclosed metallic cavity. However, existing analytical models based on coupled mode theory and finite element simulation tools are complicated to use, relatively slow to converge and fail to give researchers and system designers the intuition to optimize wireless power transfer performance. In this work a general circuit model for the cavity resonant wireless power system is introduced and validated against simulated and measured results. Results show an average agreement between the circuit model and measured transfer efficiency are within +/- 5%. Thus, cavity mode enabled wireless power transfer can be analyzed with an equivalent circuit model allowing for fast design iteration and a better understanding of how to optimize system performance. We used the circuit model developed herein to design a simple impedance matching network for 52 LED receivers and transferred power wirelessly to all of them simultaneously with approximately 30% efficiency, by combining two cavity modes, TE011 and TE012. However, under optimal load condition, which requires more complicated matching circuit, a minimum efficiency of 50% can easily be achieved at the same positions, we instead here we focused on a simple and fast design solution.