Closed-Loop Temperature Control of Nylon Artificial Muscles
We demonstrate a nested controller using temperature and position feedback to improve contraction speed, and investigate the cooling rates of various configurations that increase total force output.
October 1, 2018
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2018
Authors
Carter Haines (University of Texas at Dallas)
Gunter Niemeyer (Disney Research)
Closed-Loop Temperature Control of Nylon Artificial Muscles
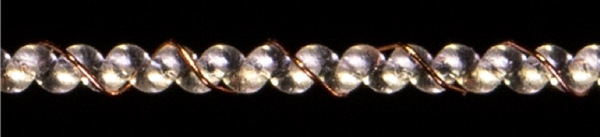
Coiled actuators made from polymer fibers are fast becoming popular due to their low-cost and ease of fabrication. Unfortunately, reliable real-time temperature measurement has been frustrated by the small fiber diameter of typical actuators. By using coiled polymer fibers wrapped with a metal wire, we demonstrate the ability to concurrently drive a muscle by electrothermal heating, and monitor muscle temperature through the wire resistance. This simple method enables convenient overheat protection for these muscles, as well as the possibility for closed-loop temperature control. Using this platform, we demonstrate a nested controller using temperature and position feedback to improve contraction speed, and investigate the cooling rates of various configurations that increase total force output.