Nonlinear Disparity Mapping for Stereoscopic 3D
This paper addresses the problem of remapping the disparity rangeof stereoscopic images and video. Such operations are highly im-portant for a variety of issues arising from the production, livebroadcast, and consumption of 3D content.
July 26, 2010
ACM SIGGRAPH 2010
Authors
Manuel Lang (Disney Research/ETH Joint PhD)
Alexander Sorkine-Hornung (Disney Research)
Oliver Wang (Disney Research)
Steven Poulakos (Disney Research/ETH Zurich)
Aljoscha Smolic (Disney Research)
Markus Gross (Disney Research/ETH Zurich)
Nonlinear Disparity Mapping for Stereoscopic 3D
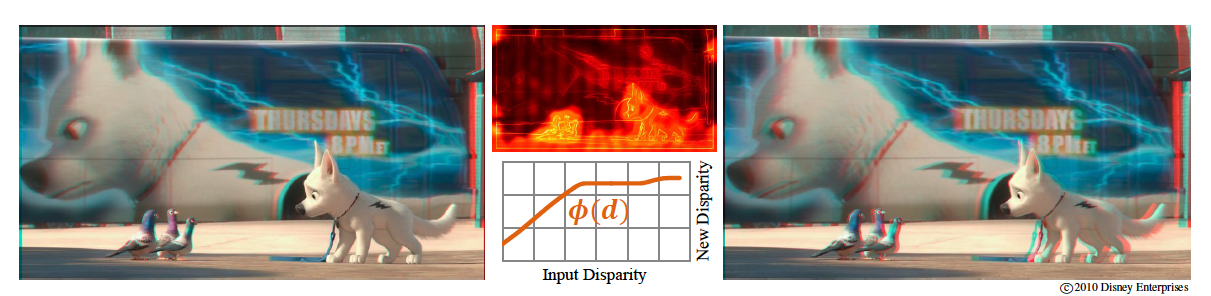
Our work is motivated by the observation that the displayed depth and the resulting 3D viewing experience are dictated by a complex combination of perceptual, technological, and artistic constraints. We first discuss the most important perceptual aspects of stereo vision and their implications for stereoscopic content creation. We then formalize these insights into a set of basic disparity mapping operators. These operators enable us to control and retarget the depth of a stereoscopic scene in a nonlinear and locally adaptive fashion. To implement our operators, we propose a new strategy based on stereoscopic warping of the input video streams. From a sparse set of stereo correspondences, our algorithm computes disparity and image-based saliency estimates, and uses them to compute a deformation of the input views so as to meet the target disparities. Our approach represents a practical solution for actual stereo production and display that does not require camera calibration, accurate dense depth maps, occlusion handling, or inpainting. We demonstrate the performance and versatility of our method using examples from live action postproduction, 3D display size adaptation, and live broadcast. An additional user study and ground truth comparison further provide evidence for the quality and practical relevance of the presented work.